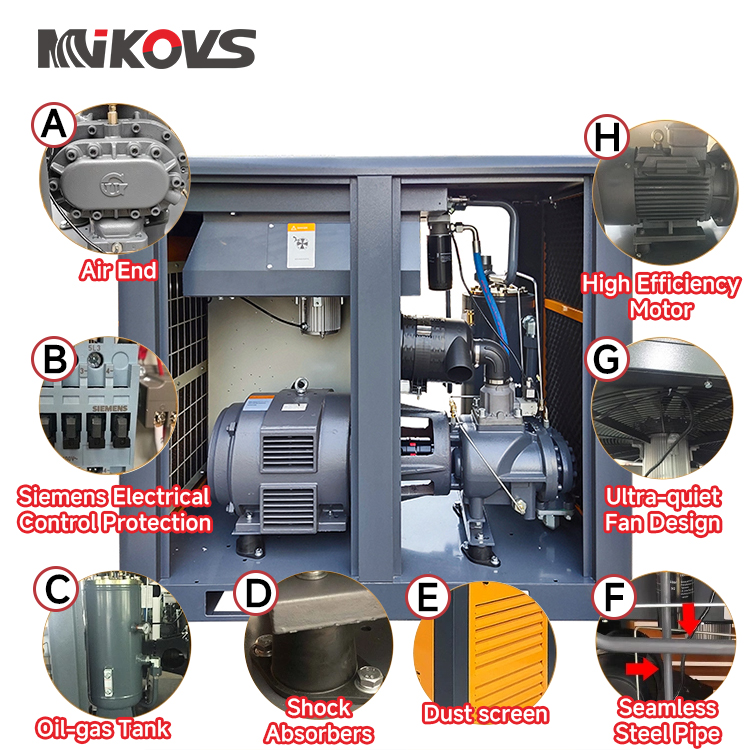
The reasons for the higher efficiency of permanent magnet motors are mainly attributed to the following:
1. High Magnetic Energy Density : Permanent magnet motors use permanent magnets to generate a magnetic field and these magnets are capable of providing high magnetic energy density, thus producing a powerful magnetic field in a smaller size and weight.
2. Reduced Energy Losses: Due to the high efficiency of permanent magnets, motors require less current to produce the same torque, which reduces copper losses (I²R losses) due to current flow.
3. High efficiency operating area: permanent magnet motors are designed so that they maintain high efficiency over a wide operating range due to the relatively constant magnetic field strength of the permanent magnets, which does not fluctuate greatly due to changes in motor load.
4. Simple structure: Permanent magnet motors usually do not require the excitation windings found in electrically excited motors, which reduces energy losses within the motor and simplifies the motor’s structure.
5. High power density: Due to the high magnetic energy density of permanent magnets, PM motors can achieve high power output in a small footprint, which means they can provide high efficiency in a compact space.
6. Good thermal performance: The design of PM motors typically allows for better thermal performance as they have fewer conductive parts and lower heat generation.
7. Reduced Maintenance: PM motors typically require less maintenance due to their simple construction, which helps to reduce downtime and improve overall operating efficiency.
8. High control accuracy: PM motors, in conjunction with modern control technology, allow for more precise speed and position control, which improves the overall efficiency of the system in applications that require precise control.
9. Energy feedback: In some applications, permanent magnet motors can also realise the feedback of braking energy, which further improves the energy efficiency of the system.
10. Long-term stability: The magnetic properties of permanent magnet materials are more stable over time, which means that motors can maintain high efficiency over long periods of operation.
Due to these advantages, PM motors are becoming increasingly popular in many modern industrial applications such as electric vehicles, wind power generation, and industrial automation equipment. However, PM motors also have some limitations, such as sensitivity to high temperatures and relatively high cost, which also need to be considered when designing and selecting motors.
Awesome! Share to:
Consult your compressor solution
With our professional products, energy-efficient and reliable compressed air solutions, perfect distribution network and long- term value-added service, we have win the trust and satisfactions from the customer all over the world.
Our Case Studies